Abstract
Review Article
So-called idiopathic scoliosis – disfiguring deformity in children, pain problems in adults. Information about biomechanical etiology, classification and therapy
Tomasz Karski*
Published: 10 March, 2020 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 016-020
In the article presented the etiology of the so-called idiopathic scoliosis (Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis [AIS]), new classification, there are given rules of therapy and causal prophylaxis. This knowledge is based on observations from 1984, but essentially from the years 1995 – 2007. In 2001 it was given the first description in classification – “S” scoliosis in 1st group / type and “C” and “S” scoliosis in 2nd A / B group and types, in 2004 “I” scoliosis in 3rd group / type.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001011 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
So-called idiopathic scoliosis; Biomechanical etiology; Classification; Therapy; Causal prophylaxis
References
- Karski T. Etiology of the so-called “idiopathic scoliosis”. Biomechanical explanation of spine deformity. Two 272 groups of development of scoliosis. New rehabilitation treatment. Possibility of prophylactics, Studies in 273 Technology and Informatics, Research into Spinal Deformities. 2002; 91: 37-46.
- Karski T, Kalakucki J, Karski J. "Syndrome of contractures" (according to Mau) with the abduction contracture of the right hip as causative factor for development of the so-called idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2006; 123: 34-39. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17108400
- Karski T. Explanation of biomechanical etiology of the so-called idiopathic scoliosis (1995 – 2007). New 276 clinical and radiological classification” in “Pohybove Ustroji”. Locomotor System. 2010; 17: 26 – 42.
- Karski Tomasz. Factores biomechanicos en la etiologia de las escoliosis dinominadas idiopaticas. Nueva 282 clasificacion. Nuevos test clinicos y nueavo tratamento conservador y profilaxis”. Cuestiones de Fisioterapia. 2010; 39: 85–152.
- Karski Tomasz. Biomechanical Etiology of the So-called Idiopathic Scoliosis (1995-2007). New Classification: 285 Three Groups, Four Sub-types. Connection with “Syndrome of Contractures”. Pan Arab J Orth Trauma. 2010; 14.
- Karski T. Biomechanical Etiology of The So-Called Idiopathic Scoliosis (1995 – 2007) – Connection with 279 “Syndrome of Contractures” – Fundamental Information for Paediatricians in Program of Early Prophylactics. / J US-China Med Sci. 2011; 8.
- Karski Tomasz. Biomechanical Etiology of the So-called Idiopathic Scoliosis (1995 - 2007). Three Groups and 288 Four Types in the New Classification. J Novel Physiotherapies. 2013; 289-290.
- Karski Jacek, Tomasz Karski. So-Called Idiopathic Scoliosis. Diagnosis. Tests Examples of Children Incorrect 291 Treated. New Therapy by Stretching Exercises and Results. J Novel Physiotherapies. 2013; 3-2.
- Karski Tomasz. Biomechanical Aetiology of the So-Called Idiopathic Scoliosis. New Classification (1995 – 2007) in Connection with “Model of Hips Movements”. Global Journal of Medical Research H: Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal System. 2014; 14.
- Karski Tomasz. Biomechanical Etiology of the So-called Idiopathic Scoliosis (1995 – 2007) - Connection with „Syndrome of Contractures” – Fundamental Information for Pediatricians in Program of Early Prophylactics. Surgical Science. 2014; 5: 33-38.
- Karski Tomasz, Karski Jacek. Syndrome of Contractures and Deformities” according to Prof. Hans Mau as Primary Cause of Hip, Neck, Shank and Spine Deformities in Babies. Youth and Adults American Research Journal of Medicine and Surgery. 2015; 1.
- Karski Tomasz, Jacek Karski. Biomechanical etiology of the so-called Idiopathic Scoliosis (1995 – 2007). Causative role of ‘’gait” and ‘’permanent standing ‘at ease’ pn the right leg”. New classification. Principles of new therapy and causal prophylaxis. Canadian Open Medical Science & Medicine Journal. 2015; 1: 1-16.
- Karski Jacek, Tomasz Karski, Jarosław Pyrc, Małgorzata Kulka. Deformations of the feet, knees, hips, pelvis in children and adults with minimal brain dysfunction causes treatment. Prophylaxis. 2016.
- Karski Tomasz, Jacek Karski. Bóle krzyża – problem neurologiczno - Objawy. Przyczyny. Leczenie. Back pain – neurology-orthopedic problems. Clinic, causes, therapy and prophylaxis. Postępy Neurologii Praktycznej, Wydawnictwo Czelej. 2016; 9 – 16.
- Karski Jacek, Karski Tomasz. “Imperfect hips” As a Problem at an Older Age. Early and Late Prophylactic Management before Arthrosis. Jacobs Journal of Physiotherapy and Exercises / USA / Texas. 2016 ; 1: 7.
- Karski Tomasz. Physiotherapy– Correct, or Incorrect, Based on ‘Wrong Principles of Treatment’. Example for Spine, Hip, Knee, Shank and Feet. 2017.
- Karski Tomasz, Jacek Karski, Klaudia Karska, Katarzyna Karska, Honorata Menet. Pediatric Prophylaxis Program of Motor System Deformations and Illnesses in Children. Problems of Spine, Hips, Knees and Feet. EC PAEDIATRICS. 2018.
- Karski Tomasz, Jacek Karski, Katarzyna Karska, Klaudia Karska, Honorata Menet. Prophylactic Rules for Newborns, Babies, Children and Adults in problems of Hip, Knee, Shank, Feet and Spin. Online J CRIMSON PUBLISHERS. 2018.
- Karski Tomasz. Biomechanical Aetiology of the So-called Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS). Lublin Classification (1995-2007). Causative Influences Connected with “Gait” and “Standing ‘at ease’ on the Right Leg”. J Orthopaedics Bone Res. 2018.
- Karski Tomasz. Biomechanical Etiology of the So-called Idiopathic Scoliosis (Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis [AIS]). New Classification Rules of Therapy and Prophylaxis. Nurs Health Care J. 2019; 4.
- Burwell G, Dangerfield PH, Lowe T, Margulies J. Spine Etiology of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Current Trends and Relevance to New Treatment Approaches. 2000; 324.
- Dangerfield PH, Dorgan JC, Scutt D, Gikas G, Taylor JF. Stature in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS).14 Meeting EPOS, Brussels. 1995.
- Green NE, Griffin PP. Hip dysplasia associated with abduction contracture of the contralateral hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1982; 64: 1273-1281. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7142235
- Gruca A, Tylman D. Patomechanika bocznych skrzywień kręgosłupa, Wydawnictwo Severus. Warszawa. 1995.
- Heikkilä E. Congenital dislocation of the hip in Finland. An epidemiologic analysis of 1035 cases. Acta Orthop Scandinavica. 1984; 55: 125-129.
- Hensinger RN. Congenital dislocation of the hip. Clinical Symp. 1979; 31: 270.
- Howorth B. The etiology of the congenital dislocation of the hip. Clin Orthop. 1977; 29: 164-179.
- Malawski Stefan. Epidemiologia skoliozy, Postępy Polskiej Spondyloortopedii. 1992.
- Malawski Stefan. Własne zasady leczenia skolioz niskostopniowych, Postępy Polskiej Spondyloortopedii. 1992.
- Malawski S. Własne zasady leczenia skolioz niskostopniowych w świetle współczesnych poglądów na etiologię i patogenezę powstawania skolioz, Chir Narz Ruchu i Ortop Pol. 1994; 3: 189-197.
- Mau H. Zur Ätiopathogenese von Skoliose, Hüftdysplasie und Schiefhals im Säuglinsalter. Zeitschrift f. 294 Orthop. 1979; 5: 601-605.
- Mau H. Die Atiopatogenese der Skoliose, Bücherei des Orthopäden, Band 33. Enke Verlag Stuttgart. 1982.
- Normelly H. Asymmetric rib growth as an aetiological factor in idiopathic scoliosis in adolescent girls, 298. Stockholm. 1985.
- Rąpała K, Tylman D. Patomechanika bocznych skrzywień kręgosłupa, Wydawnictwo Severus, Warszawa. 1995.
- Stokes IAF. Studies in Technology and Informatics, Research into Spinal Deformities. 1999; 59.
- Sevastik J, Diab K. Studies in Technology and Informatics, Research into Spinal Deformities. 1997; 37.
- Tylman D. Patomechanika bocznych skrzywień kręgosłupa, Wydawnictwo Severus, Warszawa. 1995.
- So-called idiopathic scoliosis
Figures:
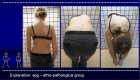
Figure 1
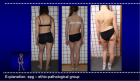
Figure 2

Figure 3
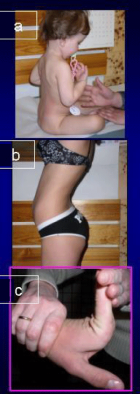
Figure 4
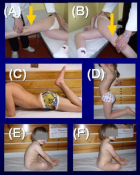
Figure 5
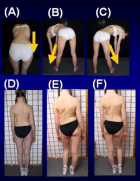
Figure 6

Figure 7
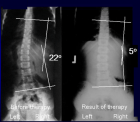
Figure 8
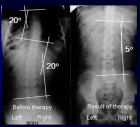
Figure 9
Similar Articles
-
Prevalence of ESBL urinary tract infection in childrenKhalil Salameh*,Galia ZA Awean,Hala Elmohamed,Hoor Alshmayt,Mohamed Riad Bur Omer . Prevalence of ESBL urinary tract infection in children. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001004; 2: 004-007
-
Aripiprazole-induced seizures in children with autism spectrum disorder and epilepsyMohammed MS Jan*. Aripiprazole-induced seizures in children with autism spectrum disorder and epilepsy. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001009; 3: 008-010
-
So-called idiopathic scoliosis – disfiguring deformity in children, pain problems in adults. Information about biomechanical etiology, classification and therapyTomasz Karski*. So-called idiopathic scoliosis – disfiguring deformity in children, pain problems in adults. Information about biomechanical etiology, classification and therapy. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001011; 3: 016-020
-
An Audit on the implementation of administering Ondansetron in children with acute gastroenteritis and its effect on admission rateSaskia D’Sa*,Ahad Hussain,Mushtaq Hussain,Zahir Afridi,John Twomey,Irfan Ahmed. An Audit on the implementation of administering Ondansetron in children with acute gastroenteritis and its effect on admission rate. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001025; 4: 023-026
-
Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulins in the prophylaxis of neonatal sepsisSharif S*,Bloomer C,Al Assaf N,Khan R. Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulins in the prophylaxis of neonatal sepsis. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001029; 4: 038-041
-
Revisiting childhood pneumonia in low-recourse setting hospitalsKarimeldin MA Salih*. Revisiting childhood pneumonia in low-recourse setting hospitals. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001035; 4: 062-066
-
Survival and predictors of mortality among HIV-infected adults receiving ART in Hawassa comprehensive specialized hospital, Sidama regional state, EthiopiaBargude Balta*,Amanuel Fanta. Survival and predictors of mortality among HIV-infected adults receiving ART in Hawassa comprehensive specialized hospital, Sidama regional state, Ethiopia. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001052; 5: 042-049
-
Delayed Diagnosis of Early-onset Sarcoidosis: A Case Report and Literature ReviewMutibah Ali Al-essi*, Lujain Salah Binkhamis, Samah Mohammed Aljohani, Nora Mohammad Alzahrani. Delayed Diagnosis of Early-onset Sarcoidosis: A Case Report and Literature Review. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001061; 7: 001-005
-
An Individual Rehabilitation and/or Habilitation Program for Children with Disabilities (IPRH)Shapovalov KA*, Shapovalova LA, Knyazeva NG, Yu PG, Toropova VS, Sannikova LА, Mezentseva AS. An Individual Rehabilitation and/or Habilitation Program for Children with Disabilities (IPRH). . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001062; 7: 007-012
-
Case Report: An Elusive Case of Septic ArthritisGeorgina George Balyorugulu*, Shabani Yusuph, Rahma Majaliwa, Mpuya Innocent, Fikiri Martine, Fatma Said, Rogatus Kabyemera, Patrick Ngoya, Jeremiah Seni. Case Report: An Elusive Case of Septic Arthritis. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001067; 7: 045-051
Recently Viewed
-
Agriculture High-Quality Development and NutritionZhongsheng Guo*. Agriculture High-Quality Development and Nutrition. Arch Food Nutr Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.afns.1001060; 8: 038-040
-
A Low-cost High-throughput Targeted Sequencing for the Accurate Detection of Respiratory Tract PathogenChangyan Ju, Chengbosen Zhou, Zhezhi Deng, Jingwei Gao, Weizhao Jiang, Hanbing Zeng, Haiwei Huang, Yongxiang Duan, David X Deng*. A Low-cost High-throughput Targeted Sequencing for the Accurate Detection of Respiratory Tract Pathogen. Int J Clin Virol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001056; 8: 001-007
-
A Comparative Study of Metoprolol and Amlodipine on Mortality, Disability and Complication in Acute StrokeJayantee Kalita*,Dhiraj Kumar,Nagendra B Gutti,Sandeep K Gupta,Anadi Mishra,Vivek Singh. A Comparative Study of Metoprolol and Amlodipine on Mortality, Disability and Complication in Acute Stroke. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001108; 9: 039-045
-
Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimesBhagat Singh*,Satish R Nailkar,Chetansen A Bhadkambekar,Suneel Prajapati,Sukhminder Kaur. Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimes. J Forensic Sci Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001043; 7: 004-010
-
A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological EnvironmentLoai Aljerf*,Nuha AlMasri. A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological Environment. Ann Adv Chem. 2018: doi: 10.29328/journal.aac.1001012; 2: 032-044
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."