Abstract
Case Report
Case Report: An Elusive Case of Septic Arthritis
Georgina George Balyorugulu*, Shabani Yusuph, Rahma Majaliwa, Mpuya Innocent, Fikiri Martine, Fatma Said, Rogatus Kabyemera, Patrick Ngoya and Jeremiah Seni
Published: 02 May, 2024 | Volume 7 - Issue 1 | Pages: 045-051
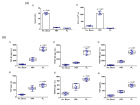
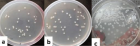
Septic arthritis is a serious inflammatory infectious state of the joint secondary to microbial infection. In the pediatric population the most common route of infection is haematogenous spread. Less than fifty percent of patients with septic arthritis will yield positive culture results with a mortality rate of up to 42% in some cases. Due to the challenge in obtaining culture and identification of the causative organism the management of septic arthritis has been more of empirical in nature with the chosen antibiotic synchronized with the epidemiological data. Here is a case of a 14 months old female patient presenting at our hospital with a left knee and lower thigh swelling for three days with failure to bare weight on the limb. In addition, she had fever and diarrhea for three days. Upon evaluation clinical, laboratory and radiological findings supported septic arthritis expect for her blood, pus and synovial fluid culture of which all came back negative. She had poor response to intravenous ceftriaxone, gentamycin, metronidazole, ampicillin- cloxacillin and amoxicillin clavunate. Over the course of therapy, she developed septic shock, severe anemia and acute liver failure and was admitted to the intensive care unit. Afterwards she was initiated vancomycin and developed a hypersensitivity reaction with generalized edema which prompted cessation of the drug. Due to her critical state and poor response a triple therapy regimen composing of meropenem, ciprofloxacin and metronidazole was selected and maintained for three weeks followed by an oral clindamycin course for another three weeks of which she responded. In addition, surgical debridement arthrotomy, irrigation and drainage were done. Physiotherapy for rehabilitation is ongoing with patient recovering well.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001067 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Antibiotics; Culture; Fastidious organisms; Pediatric
References
- Krogstad P. Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis In: Feigin RD, Cherry JD, editors Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases 6th ed Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2009; 725–748.
- Lavy CB, Peek AC, Manjolo G. The incidence of septic arthritis in Malawian children. Int Orthop. 2005 Jun;29(3):195-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-005-0643-9. Epub 2005 Apr 2. PMID: 15806359; PMCID: PMC3456879.
- Nunn TR, Cheung WY, Rollinson PD. A prospective study of pyogenic sepsis of the hip in childhood. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007 Jan;89(1):100-6. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.89B1.17940. PMID: 17259425.
- Welkon CJ, Long SS, Fisher MC, Alburger PD. Pyogenic arthritis in infants and children: a review of 95 cases. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;5(6):669-76. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198611000-00014. PMID: 3540888.
- Castellazzi L, Mantero M, Esposito S. Update on the Management of Pediatric Acute Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 1;17(6):855. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060855. PMID: 27258258; PMCID: PMC4926389.
- Khattak M, Vellathussery Chakkalakumbil S, Stevenson RA, Bryson DJ, Reidy MJ, Talbot CL, et al. Kingella kingae septic arthritis. Bone Joint J. 2021 Mar;103-B(3):584-8.
- Yagupsky P. Changing aetiology of paediatric septic arthritis. J Paediatr Child Health. 2021 Oct;57(10):1560-1563. doi: 10.1111/jpc.15654. Epub 2021 Jul 14. PMID: 34259365.
- al-Salem AH, Ahmed HA, Qaisaruddin S, al-Jam'a A, Elbashier AM, al-Dabbous I. Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis in sickle cell disease in the eastern province of Saudi Arabia. Int Orthop. 1992;16(4):398-402. doi: 10.1007/BF00189627. PMID: 1473897.Nduati RW, Wamola IA Bacteriology of acute septic arthritis Journal of tropical pediatrics 1991 Aug 1;37(4):172-5.
- Lavy CB, Lavy VR, Anderson I. Salmonella septic arthritis of the shoulder in Zambian children. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1996 Jun;41(3):197-9. PMID: 8763188.
- Molyneux E, French G. Salmonella joint infection in Malawian children. J Infect. 1982 Mar;4(2):131-8. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(82)93701-x. PMID: 6764502.
- Peltola H, Pääkkönen M, Kallio P, Kallio MJ; OM-SA Study Group. Clindamycin vs. first-generation cephalosporins for acute osteoarticular infections of childhood--a prospective quasi-randomized controlled trial. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012 Jun;18(6):582-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03643.x. Epub 2011 Oct 19. PMID: 22011265.
- Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, J Rybak M, Talan DA, Chambers HF; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of america for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Feb 1;52(3):e18-55. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq146. Epub 2011 Jan 4. Erratum in: Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Aug 1;53(3):319. PMID: 21208910.
- Saphyakhajon P, Joshi AY, Huskins WC, Henry NK, Boyce TG. Empiric antibiotic therapy for acute osteoarticular infections with suspected methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or Kingella. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008 Aug;27(8):765-7. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31816fc34c. PMID: 18600193.
- Sherman JW, Conte JE Jr. Ceftriaxone treatment of multidrug-resistant Salmonella osteomyelitis. Am J Med. 1987 Jul;83(1):137-8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90508-0. PMID: 3605165.
- Bradley JS, Jackson MA; Committee on Infectious Diseases; American Academy of Pediatrics. The use of systemic and topical fluoroquinolones. Pediatrics. 2011 Oct;128(4):e1034-45. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-1496. Epub 2011 Sep 26. PMID: 21949152.
- Yagupsky P, Porsch E, St Geme JW 3rd. Kingella kingae: an emerging pathogen in young children. Pediatrics. 2011 Mar;127(3):557-65. doi: 10.1542/peds.2010-1867. Epub 2011 Feb 14. PMID: 21321033.
- Ilharreborde B, Bidet P, Lorrot M, Even J, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Liguori S, Vitoux C, Lefevre Y, Doit C, Fitoussi F, Penneçot G, Bingen E, Mazda K, Bonacorsi S. New real-time PCR-based method for Kingella kingae DNA detection: application to samples collected from 89 children with acute arthritis. J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Jun;47(6):1837-41. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00144-09. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Erratum in: J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Sep;47(9):3071. PMID: 19369442; PMCID: PMC2691089.
- Basmaci R, Ilharreborde B, Bidet P, Doit C, Lorrot M, Mazda K, Bingen E, Bonacorsi S. Isolation of Kingella kingae in the oropharynx during K. kingae arthritis in children. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012 May;18(5):E134-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03799.x. Epub 2012 Mar 6. PMID: 22390653.
- Dodwell ER. Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis in children: current concepts. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2013 Feb;25(1):58-63. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e32835c2b42. PMID: 23283291.
- Russell CD, Ramaesh R, Kalima P, Murray A, Gaston MS. Microbiological characteristics of acute osteoarticular infections in children. J Med Microbiol. 2015 Apr;64(Pt 4):446-453. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000026. Epub 2015 Jan 16. PMID: 25596125.
- Spyridakis E, Gerber JS, Schriver E, Grundmeier RW, Porsch EA, St Geme JW, Downes KJ. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Children with Culture-Negative Septic Arthritis. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2019 Jul 1;8(3):228-234. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piy034. PMID: 29718310.
- Pääkkönen M, Kallio MJ, Kallio PE, Peltola H. Sensitivity of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in childhood bone and joint infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010 Mar;468(3):861-6. doi: 10.1007/s11999-009-0936-1. Epub 2009 Jun 17. PMID: 19533263; PMCID: PMC2816763.
- Stans AA. Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis In: Lovell and Winter's Pediatric Orthopaedics, 6th ed, Morrissy RT, Weinstein SL (Eds), Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia. 2006; 440.
- Kallio MJ, Unkila-Kallio L, Aalto K, Peltola H. Serum C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and white blood cell count in septic arthritis of children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997 Apr;16(4):411-3. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199704000-00015. PMID: 9109146.
- Kallio MJ, Unkila-Kallio L, Aalto K, Peltola H. Serum C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and white blood cell count in septic arthritis of children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997 Apr;16(4):411-3. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199704000-00015. PMID: 9109146.
- Wiley JJ, Fraser GA. Septic arthritis in childhood. Can J Surg. 1979 Jul;22(4):326-30. PMID: 313236.
- Nade S, Robertson FW, Taylor TK. Antibiotics in the treatment of acute osteomyelitis and acute septic arthritis in children. Med J Aust. 1974 Nov 9;2(19):703-5. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb71104.x. PMID: 4444617.
- Ahvonen P, Sievers K, Aho K. Arthritis associated with Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1969;15(3):232-53. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1969.15.issue-1-4.32. PMID: 4902690.
- Rohekar S, Pope J. Epidemiologic approaches to infection and immunity: the case of reactive arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009 Jul;21(4):386-90. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32832aac66. PMID: 19373091.
- Pope JE, Krizova A, Garg AX, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Ouimet JM. Campylobacter reactive arthritis: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Aug;37(1):48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.12.006. Epub 2007 Mar 13. PMID: 17360026; PMCID: PMC2909271.
- Coath FL, Mackay J, Gaffney JK. Axial presentation of reactive arthritis secondary to COVID-19 infection. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Jul 1;60(7):e232-e233. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab009. PMID: 33471106; PMCID: PMC7928576.
- Mathew AJ, Ravindran V. Infections and arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014 Dec;28(6):935-59. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 May 27. PMID: 26096095.
- García-Kutzbach A, Chacón-Súchite J, García-Ferrer H, Iraheta I. Reactive arthritis: update 2018. Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Apr;37(4):869-874. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4022-5. Epub 2018 Feb 17. PMID: 29455267.
- Piussan C, Pautard-Muchemble B, Pautard JC, Lenaerts C, Boudailliez B, Risbourg B. Les arthrites réactionnelles de l'enfant [Reactive arthritis in children]. Sem Hop. 1984 Jan 12;60(1):52-62. French. PMID: 6320436.
- Arnett FC. Incomplete Reiter's syndrome: clinical comparisons with classical triad. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979;38 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):suppl 73-8. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.suppl_1.73. PMID: 318103; PMCID: PMC1049089.
- Coakley G, Mathews C, Field M, Jones A, Kingsley G, Walker D, Phillips M, Bradish C, McLachlan A, Mohammed R, Weston V; British Society for Rheumatology Standards, Guidelines and Audit Working Group. BSR & BHPR, BOA, RCGP and BSAC guidelines for management of the hot swollen joint in adults. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Aug;45(8):1039-41. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kel163a. Epub 2006 Jul 6. PMID: 16829534.
- Kaandorp CJ, Krijnen P, Moens HJ, Habbema JD, van Schaardenburg D. The outcome of bacterial arthritis: a prospective community-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 May;40(5):884-92. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400516. PMID: 9153550.
- Fangtham M, Baer AN. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus arthritis in adults: case report and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Feb;41(4):604-10. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.06.018. Epub 2011 Oct 28. PMID: 22035623.
- Omoke NI, Obasi AA. Childhood Pyogenic Septic Arthritis as Seen in a Teaching Hospital South East Nigeria. Niger J Surg. 2017 Jan-Jun;23(1):26-32. doi: 10.4103/1117-6806.199968. PMID: 28584508; PMCID: PMC5441212.
- Kendal J. Septic Arthritis: Pathogenesis and clinical findings. 2014. wwwcalgaryguidecom.
- McCarthy JJ, Dormans JP, Kozin SH, Pizzutillo PD. Musculoskeletal infections in children: basic treatment principles and recent advancements. Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:515-28. PMID: 15948476.
- Akinyoola AL, Obiajunwa PO, Oginni LM. Septic arthritis in children. West Afr J Med. 2006 Apr-Jun;25(2):119-23. doi: 10.4314/wajm.v25i2.28260. PMID: 16918182.
Figures:
Similar Articles
-
Congenital poisoning after maternal parenteral mercury administrationBenjamin Courchia*,Leventer Roberts Maya,Meyer John,Galvez Maida,Herrera Jaime,Rauch Daniel. Congenital poisoning after maternal parenteral mercury administration. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001001; 1: 001-005
-
The Impact of Adenotonsillectomy on Health-Related Quality of Life in Paediatric PatientsShuaib Kayode Aremu*. The Impact of Adenotonsillectomy on Health-Related Quality of Life in Paediatric Patients. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001002; 1: 006-011
-
Glycemic status and its effect in Neonatal Sepsis - A prospective study in a Tertiary Care Hospital in NepalBadri Kumar Gupta*,Binod Kumar Gupta,Amit Kumar Shrivastava,Pradeep Chetri. Glycemic status and its effect in Neonatal Sepsis - A prospective study in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Nepal. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001006; 2: 015-019
-
Aripiprazole-induced seizures in children with autism spectrum disorder and epilepsyMohammed MS Jan*. Aripiprazole-induced seizures in children with autism spectrum disorder and epilepsy. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001009; 3: 008-010
-
Case-based education to improve learning and faculty teaching of residents and students in a clinical settingDiane E Lorant*,Elizabeth A Wetzel. Case-based education to improve learning and faculty teaching of residents and students in a clinical setting. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001010; 3: 011-015
-
“Syndrome of Contractures and Deformities” according Prof. Hans Mau. Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment: Recommendations for parentsTomasz Karski*,Jacek Karski. “Syndrome of Contractures and Deformities” according Prof. Hans Mau. Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment: Recommendations for parents. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001012; 3: 021-023
-
The practice of self-medication in children by their mothers in Lubumbashi, Democratic Republic of CongoOlivier Mukuku*,Astrid Mukemo Katumbo,Thierry Sonny Tshiningi,Judith Sangwa Sinanduku,Loriot Kayinga Mudisu,Peggy Mulunda Mwadi,Oscar Numbi Luboya,Françoise Kaj Malonga. The practice of self-medication in children by their mothers in Lubumbashi, Democratic Republic of Congo. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001014; 3: 027-031
-
A rare case report on pediatric shellfish allergyBetsy Mathew*,Ananta Jois. A rare case report on pediatric shellfish allergy. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001018; 3: 056-057
-
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): A case with adverse reaction to three drugs alternately administeredSergio Manieri*,Maria P Mirauda,Fabiola De Gregorio,Carmela Colangelo,Maria Tagliente,Rosaria Abate,Luciana Romaniello,Rosa Lapolla,Donatello Salvatore. Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): A case with adverse reaction to three drugs alternately administered. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001022; 4: 001-005
-
Rationality and irrationality in the use of antibiotics in the epiclatino Latin American Neonatal UnitsAngela B Hoyos*. Rationality and irrationality in the use of antibiotics in the epiclatino Latin American Neonatal Units. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.japch.1001028; 4: 035-037
Recently Viewed
-
Maternal and perinatal outcomes of uterine rupture in Lubumbashi, Democratic Republic of CongoJacques Ngoy Kitenge,Olivier Mukuku*,Xavier K Kinenkinda,Prosper L Kakudji. Maternal and perinatal outcomes of uterine rupture in Lubumbashi, Democratic Republic of Congo. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001067; 3: 136-141
-
Effect of sperm DNA fragmentation on ICSI outcome: A prospective studySaravanan Lakshamanan,Saravanan Mahalakshmi,Harish Ramya,Sharma Nidhi*. Effect of sperm DNA fragmentation on ICSI outcome: A prospective study. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001065; 3: 127-131
-
Forensic analysis of private browsing mechanisms: Tracing internet activitiesHasan Fayyad-Kazan*,Sondos Kassem-Moussa,Hussin J Hejase,Ale J Hejase. Forensic analysis of private browsing mechanisms: Tracing internet activities. J Forensic Sci Res. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001022; 5: 012-019
-
A study of coagulation profile in patients with cancer in a tertiary care hospitalGaurav Khichariya,Manjula K*,Subhashish Das,Kalyani R. A study of coagulation profile in patients with cancer in a tertiary care hospital. J Hematol Clin Res. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001015; 5: 001-003
-
Viral meningitis in pregnancy: A case reportRuth Roseingrave*,Savita Lalchandani . Viral meningitis in pregnancy: A case report. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001063; 3: 121-122
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."